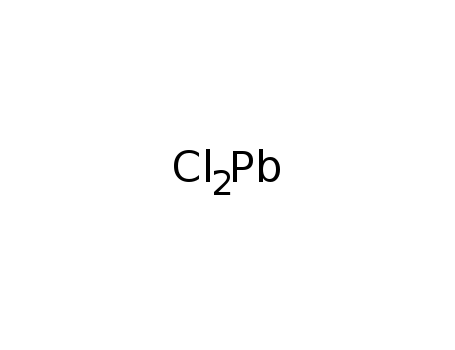- Molecular Formula: PbCl2
- CasNo.: 7758-95-4
- Melting point: 501 °C(lit.)
- Appearance: white crystals or powder
- ProductionCapacity:
- Purity:
- Packing:
-
Product Details:
Top Purity Factory Supply 99.99%-99.999% Lead Chloride 7758-95-4 with Safe Delivery
- Molecular Formula:Cl2Pb
- Molecular Weight:278.106
- Appearance/Colour:white crystals or powder
- Vapor Pressure:1 mm Hg ( 547 °C)
- Melting Point:501 °C(lit.)
- Boiling Point:950°C(lit.)
- Flash Point:951°C
- PSA:0.00000
- Density:5.85g/mLat 25°C(lit.)
- LogP:-6.37280
Lead dichloride(Cas 7758-95-4) Usage
Reactions
Lead(II) chloride reacts with chlorine to produce Lead(IV) chloride: PbCl2+ Cl2→PbCl4.
Preparation
Lead dichloride is precipitated by adding hydrochloric acid or any chloride salt solution to a cold solution of lead nitrate or other lead(II) salt: Pb2+ + 2Clˉ → PbCl2 Alternatively, it is prepared by treating lead monoxide or basic lead carbonate with hydrochloric acid and allowing the precipitate to settle..
Reactivity Profile
Lead dichloride is a weak reducing agent. Interaction of Lead dichloride and calcium is explosive on warming, [Mellor, 1941, Vol. 3, 369].
Hazard
Toxic effects from ingestion may vary from low to moderate. The oral lethal dose in guinea pigs is documented as 1,500 mg/kg. (Lewis (Sr.), R. J. 1996. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold).
Health Hazard
DUST AND FUMES. POISONOUS IF INHALED. SOLID: If swallowed, may cause metallic taste, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Fire Hazard
Not flammable. POISONOUS METAL FUMES MAY BE PRODUCED IN FIRE. Toxic metal fumes. Can emit toxic metal fumes.
Flammability and Explosibility
Notclassified
Potential Exposure
Used to make lead salts; lead chromate pigments; as an analytical reagent for making other chemicals; making printed circuit boards; as a solder and flux.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from distilled water at 100o (33mL/g) after filtering through sintered-glass and adding a few drops of HCl, by cooling. After three crystallisations the solid is dried under vacuum or under anhydrous HCl vapour by heating slowly to 400o. The solubility in H2O is 0.07% at ~10o, and 0.43% at ~ 100o.
Incompatibilities
A reducing agent. Violent reaction with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, and chemically active metals. Explosive with calcium 1 warming
Physical properties
White orthorhombic crystals; refractive index 2.199; density 5.85 g/cm3; melts at 501°C; vaporizes at 950°C; partially soluble in cold water (6.73 g/L at 0°C and 9.9 g/L at 20°C); KSP 1.17x10-5 at 25°C; moderately soluble in boiling water (33.4 g/L at 100°C); slightly soluble in dilute HCl and ammonia; insoluble in alcohol.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride consisting of two chlorine atoms covalently bound to a central lead atom.
General Description
Prepared by reacting lead(II) oxide /acetate or carbonate with HCl. In crystalline PbCl2, each atom is coordinated by nine Cl atoms, six of which lie at the apices of a trigonal prism and the remaining three beyond the centers of the three prism faces. Each Cl is coordinated by four or five Pb atoms. Upon exposure to air it form basic chlorides such as PbCl2.Pb(OH)2.
InChI:InChI=1/2ClH.Pb.4H/h2*1H;;;;;/q;;+2;;;;/p-2/r2ClH.H4Pb/h2*1H;1H4/q;;+2/p-2
7758-95-4 Relevant articles
Reactions of tin and lead with tricarbonylcyclopentadienylmolybdenum(II) and tricarbonylcyclopentadienyltungsten(II) chlorides
Piskunov,Maslennikov,Spirina,Maslennikov,Artemov
, p. 65 - 67 (2002)
Tin was oxidized with tricarbonylcyclope...
Thermal transformation of 1D-Pb(en)2Cl2to 3D-PbCl2 via 2D-Pb(en)Cl2and their substantial modification of the coordination environment on Pb(II)
Cho, Yoonsuk,Kim, Seonhong,Pyo, Seugmoon,Park, Yong Sun,Kim, Seung-Joo,Yun, Hoseop,Do, Junghwan
, p. 2105 - 2110 (2010)
The solvothermal synthesis and crystal s...
Ba6BO3Cl9and Pb6BO4Cl7: structural insights intoortho-borates with uncondensed BO4tetrahedra
Li, Wei,Wu, Hongping,Yu, Hongwei,Hu, Zhanggui,Wang, Jiyang,Wu, Yicheng
, p. 6086 - 6089 (2020)
Two new halogen-richortho-borates, Ba6BO...
Molecular Structures of Monomeric Gallium Trichloride, Indium Trichloride and Lead Tetrachloride by Gas Electron Diffraction
Haaland, Arne,Hammel, Andreas,Martinsen, Kjell-Gunnar,Tremmel, Janos,Volden, Hans Vidar
, p. 2209 - 2214 (1992)
Gas electron diffraction data for monome...
A Monoaryllead Trichloride That Resists Reductive Elimination
Olaru, Marian,Kather, Ralf,Hupf, Emanuel,Lork, Enno,Mebs, Stefan,Beckmann, Jens
, (2018)
Transmetallation of Pb(OAc)4 with R2Hg (...
Organized assemblies of lead(II) complexes of a tetraiminodiphenol macrocyclic ligand: Manifestation of weak metal-anion interactions and the directional influence of anions
Dutta, Bula,Adhikary, Bibhutosh,Bag, Pradip,Floerke, Ulrich,Nag, Kamalaksha
, p. 2760 - 2767 (2002)
The syntheses and crystal structures of ...
The synthesis, characterization, and theoretical analysis of (NH4)3PbCl5
Zhu, Liang,Jin, Wenqi,Yang, Zhihua,Yang, Yun,Pan, Shilie
, p. 2038 - 2043 (2021)
A new compound, namely (NH4)3PbCl5, has ...
The first salt of an isolated pentachloroplumbate(II) trianion
Kalf, Irmgard,Englert, Ulli
, p. m129-m131 (2006)
The title compound, tris(cyclohexane-1,2...
FCC-HCP phase boundary in lead
Kuznetsov,Dmitriev,Dubrovinsky,Prakapenka,Weber
, p. 125 - 127 (2002)
The temperature evolution of fcc-to-hcp ...
Kinetic Study of the Reactions between Lead Metal and Hydrogen Bromide and Hydrogen Chloride
Harrison, Philip G.,Holt, Grenville
, p. 1027 - 1032 (1992)
The kinetic of the reactions between gas...
Copper polytellurite-chlorides with A2?+ cations ([Formula presented], Pb) obtained by CVT reactions
Zinyakhina, Diana O.,Siidra, Oleg I.,Charkin, Dmitri O.,Nazarchuk, Evgeniy V.,Bubnova, Rimma S.
, p. 94 - 97 (2016)
Two novel polytellurite-chlorides Pb5Cu2...
Novel cubic gravel-like EDAPbCl4@ZIF-67 as electrochemical sensor for the detection of protocatechuic acid
Chen, Kaixuan,Li, Shuji,Luo, Shiping,Song, Ningning,Su, Zilong,Wang, Jiajun,Xie, Aijuan,Yang, Yun,Zhu, Shichao
, (2022/02/03)
A novel EDAPbCl4 @ZIF-67 (EDA = ethylene...
7758-95-4 Process route
-

-
lead(II) sulfide
-
- 7782-50-5
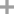
chlorine

-
- 10025-67-9
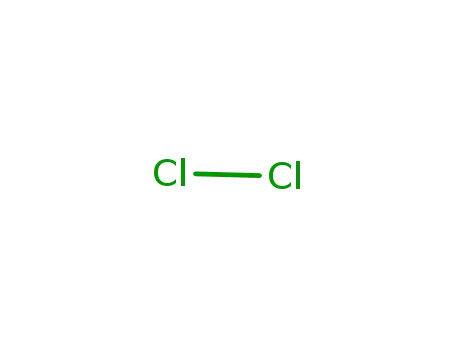
disulfur dichloride

-
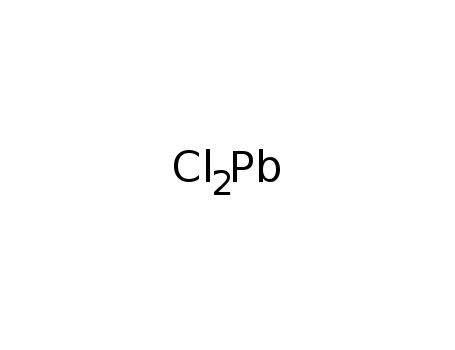
- 7758-95-4
lead(II) chloride
ConditionsConditions Yield In neat (no solvent); slow reaction of PbS and Cl2 without evolution of heat;;-

- 7439-92-1
lead

-
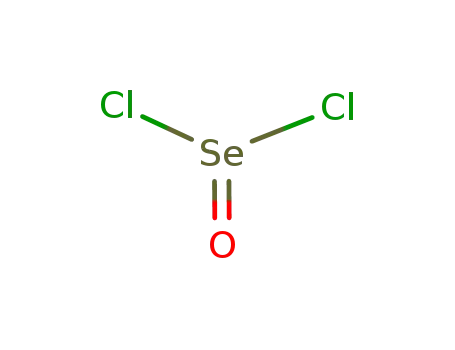
- 7791-23-3
selenium oxychloride

-
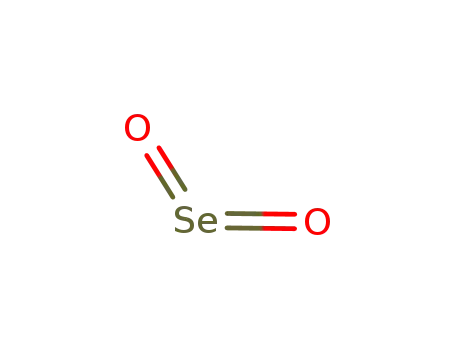
- 7446-08-4
selenium(IV) oxide

-
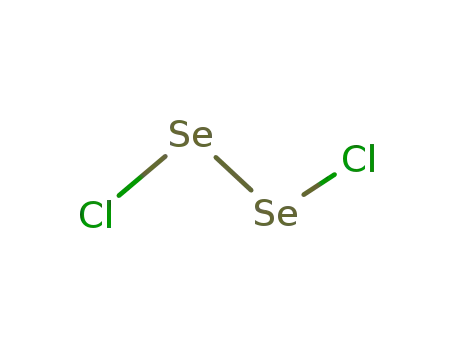
- 10025-68-0
diselenium dichloride

-
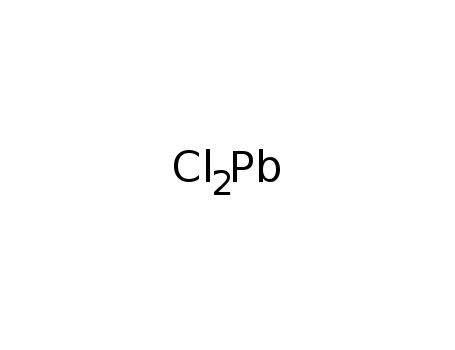
- 7758-95-4
lead(II) chloride
ConditionsConditions Yield In neat (no solvent);In neat (no solvent);7758-95-4 Upstream products
-
7791-25-5
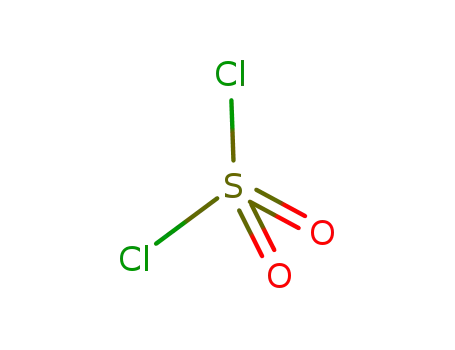
sulfuryl dichloride
-
7439-92-1

lead
-
12128-23-3
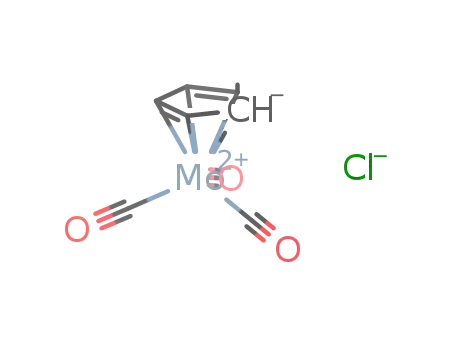
tricarbonylcyclopentadienylmolybdenum(II) chloride
-
2696-92-6
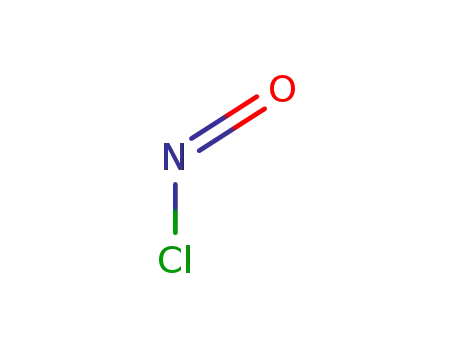
nitrosylchloride
7758-95-4 Downstream products
-
148877-97-8
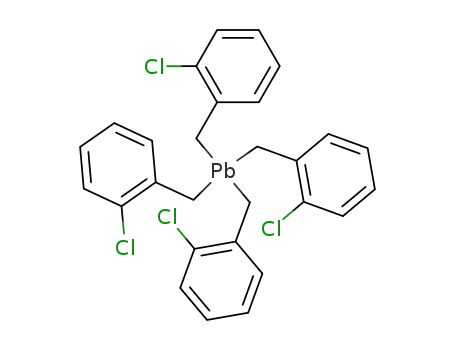
tetrakis(2-chlorobenzyl)lead
-
7704-34-9

sulfur
-
110486-49-2
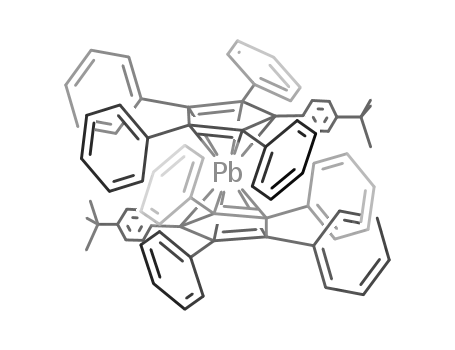
Di-t-butyldecaphenylplumbocen
-
89036-49-7
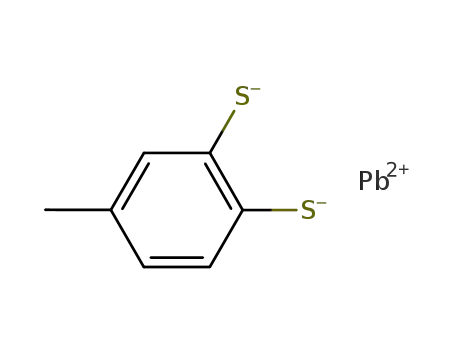
{Pb(C7H6S2)}